Advanced Matrix Multiplication Optimization on Modern Multi-Core Processors
Key Takeaways
- The core work is an optimized, multi-threaded FP32 matrix multiplication implementation written in pure C, utilizing FMA3 and AVX2 vector instructions.
- The implementation aims to achieve performance comparable to established BLAS libraries without relying on low-level assembly code.
- Achieving peak performance requires manual fine-tuning of hyperparameters such as thread count, kernel size, and tile sizes.
- Matrix multiplication is a fundamental operation in modern neural networks, often relying on external, highly optimized BLAS libraries.
- The author benchmarked the code on an AMD Ryzen 7 9700X and plans to compare its performance against OpenBLAS.
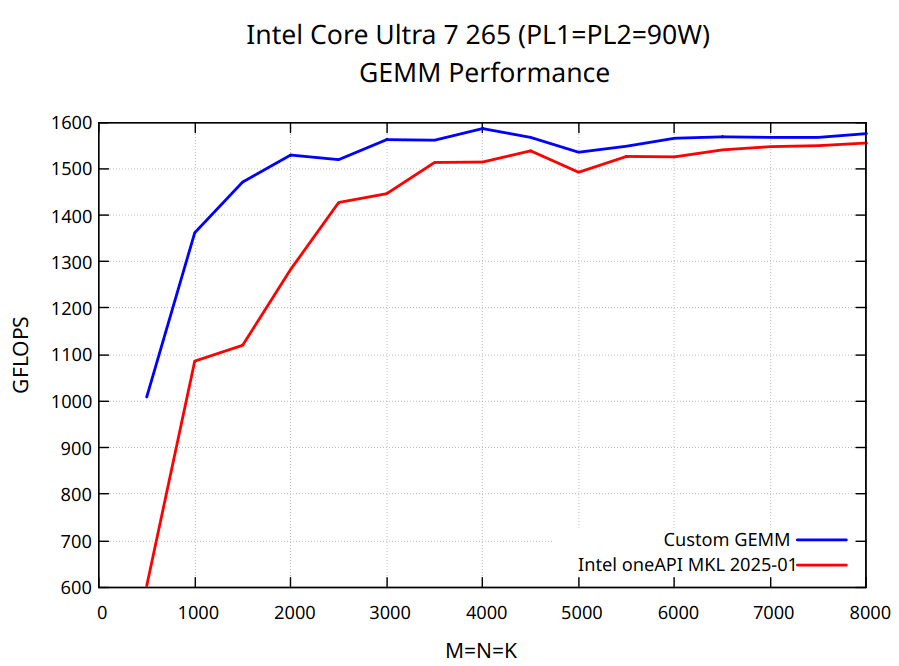
This article presents a custom implementation of multi-threaded FP32 matrix multiplication written entirely in pure C, designed to run efficiently across modern x86-64 processors using FMA3 and AVX2 vector instructions. The goal was to create a solution that is simple, extensible, and competitive with established Basic Linear Algebra Subprograms (BLAS) libraries such as OpenBLAS and Intel MKL, which often use low-level assembly optimization. The author notes that achieving maximum performance necessitates careful tuning of several hyperparameters, including kernel and tile sizes, and mentions that AVX-512 CPUs might see better results from libraries that utilize those specific instructions. The implementation draws inspiration from high-performance designs found in papers related to GotoBLAS and the BLIS library. The post also outlines the hardware used for benchmarking, including an AMD Ryzen 7 9700X, and sets the stage for a step-by-step comparison against OpenBLAS.


